Fasting from dawn until sunset is a regular practice during Ramadan. However, for individuals managing diabetes, this abstinence from food and drink can cause fluctuations in blood glucose levels. To sustain energy levels and nourish the body, rituals include pre-dawn meals and evening feasts. However, for individuals with diabetes, these meals require careful consideration to prevent any sudden spikes or drops.
According to Dr. Pankaj Aneja, Diabetologist, Director – Diabetes & Metabolic Diseases, Max Super Speciality Hospital, Delhi, “Alongside a well-balanced nutritional plan, regular monitoring is important for people living with diabetes. Accurate and real-time blood glucose readings can be constantly tracked with the help of prick-free devices like continuous glucose monitoring (CGM). This combination of a balanced diet and regular monitoring is essential for those fasting during this time, ensuring effective management of blood glucose levels throughout the holy month.”
Healthy practices for maintaining blood sugar levels during Ramadan
Properly recharge your body with nutrients during Iftar:
According to tradition, the fast is broken with dates and fruits, which is followed by a proper balanced meal. Make sure to drink water and hydrate yourself well, and avoid highly caffeinated or sugary drinks like coffee, tea, and soft drinks. It is important to have a stable meal plan striking a balance between intake of carbohydrates, protein, and fats. Have more nutrients and fiber-rich starchy foods like oats, multigrain breads, vegetables, lentils (dal), and proteins like fish, tofu, and nuts.

Additionally, you can have diabetes-specific oral nutritional supplements as an evening snack during Iftar (or even at the time of Sehri). Such scientifically formulated supplements, with high-quality protein and vital nutrients, have a slow-release energy system which helps manage one’s blood glucose, hunger, and energy levels. Consult your doctor to select the right solutions for your nutritional needs.
Keep your body moving:
Physical activity is as important as proper diabetes nutrition, it is also essential to maintain good health. In addition to eating right during fasting, staying fit through regular exercise is a great way to manage diabetes. It’s recommended to avoid overexertion and aggressive workouts (especially during the last few hours of fasting). Instead, just do simple workouts of around 30 minutes. This could include walking or yoga.
Improve your sleep schedule:
Ramadan often involves staying up late with friends and family. However, getting adequate hours of good-quality sleep is crucial in maintaining good health. It also helps people avoid sleep deprivation, which can negatively impact your hunger or craving levels. Also, sleep plays an important role in supporting immunity, metabolism, and regulating blood glucose levels, which is essential when managing diabetes.
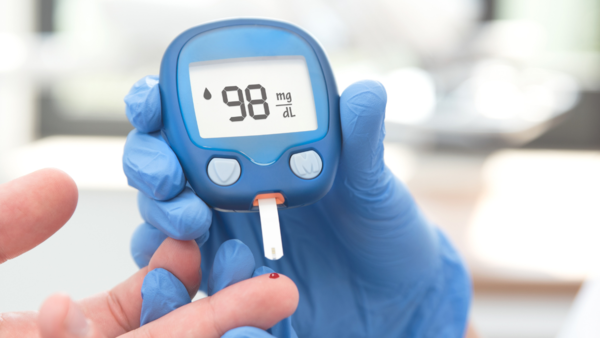
Regularly monitor blood glucose levels:
It is extremely important to consistently check your blood glucose levels. CGM devices support real-time glucose monitoring instead of capturing blood sugar levels at a particular point in time. The data is easily accessible on your smartphone, too, and can support easier decision-making related to food, physical activity, and therapy. Utilizing data from these devices can enable individuals to take corrective actions with the meal plan and maintain health during this period.
No gym required! Yoga for a flat stomach by Himalayan Siddhaa Akshar